Engineer’s Codex is a free, weekly publication distilling real-world software engineering.
Read the discussion on Reddit or Hacker News.
In January 2012, Pinterest hit 11.7 million monthly unique users with only 6 engineers.
Having launched in March 2010, it was the fastest company to race past 10 million monthly users at the time.
Pinterest is an image-heavy social network, where users can save or “pin” images to their boards.
When I say “users” below, I mean “monthly active users” (MAUs).
- Use known, proven technologies. Pinterest’s dive into newer technologies at the time led to issues like data corruption.
- Keep it simple. (A recurring theme!)
- Don’t get too creative. The team settled on an architecture where they could add more of the same nodes to scale.
- Limit your options.
- Sharding databases > clustering. It reduced data transfer across nodes, which was a good thing.
- Have fun! New engineers would contribute code in their first week.
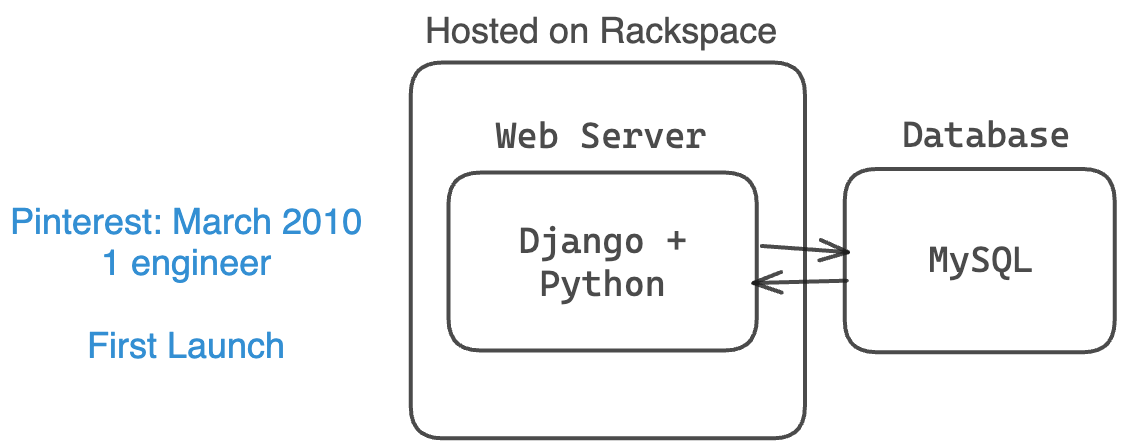
Pinterest launched in March 2010 with 1 small MySQL database, 1 small web server, and 1 engineer (along with the 2 co-founders).
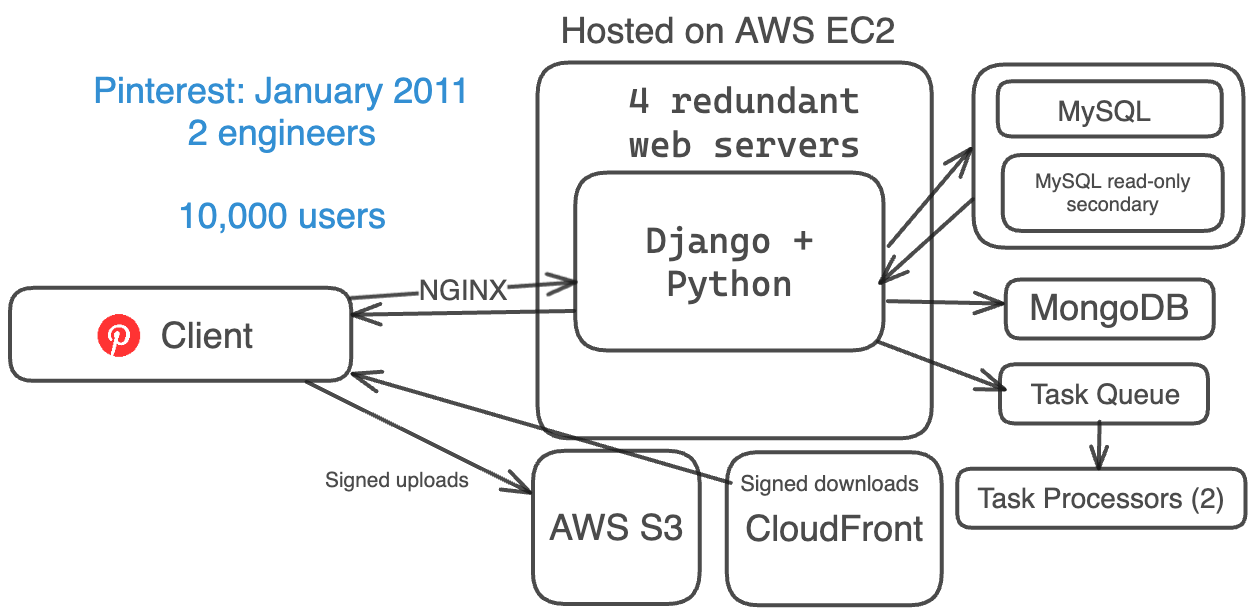
Nine months later in January 2011, Pinterest’s architecture had evolved to handle more users. They were still invite-only and had 2 engineers.
They had:
- a basic web server stack (Amazon EC2, S3, and CloudFront)
- Django (Python) for their backend
- 4 web servers for redundancy
- NGINX as their reverse proxy and load balancer.
- 1 MySQL database at this point + 1 read-only secondary
- MongoDB for counters
- 1 task queue and 2 task processors for asynchronous tasks
From January 2011 to October 2011, Pinterest grew extremely fast, doubling users every month and a half.
Their iPhone app launch in March 2011 was one of the factors fueling this growth.
When things grow fast, technology breaks more often than you expect.
Pinterest made a mistake: they over-complicated their architecture immensely.
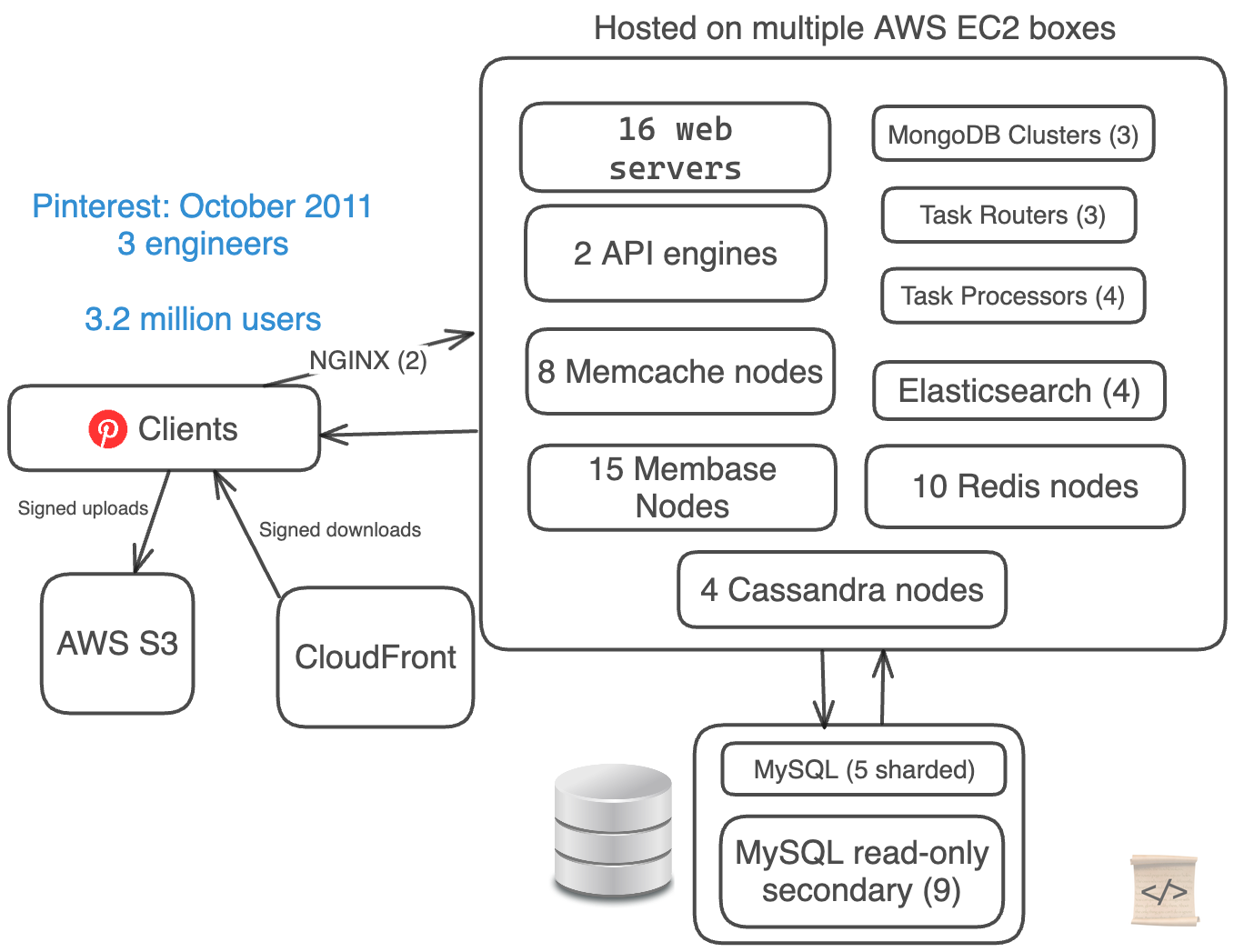
They had only 3 engineers, but 5 different database technologies for their data.
They were both manually sharding their MySQL databases and clustering their data using Cassandra and Membase (now Couchbase).
- Web server stack (EC2 + S3 + CloudFront)
- 16 web servers
- 2 API engines
- 2 NGINX proxies
- 5 manually-sharded MySQL DBs + 9 read-only secondaries
- 4 Cassandra Nodes
- 15 Membase Nodes (3 separate clusters)
- 8 Memcache Nodes
- 10 Redis Nodes
- 3 Task Routers + 4 Task Processors
- 4 Elastic Search Nodes
- 3 Mongo Clusters
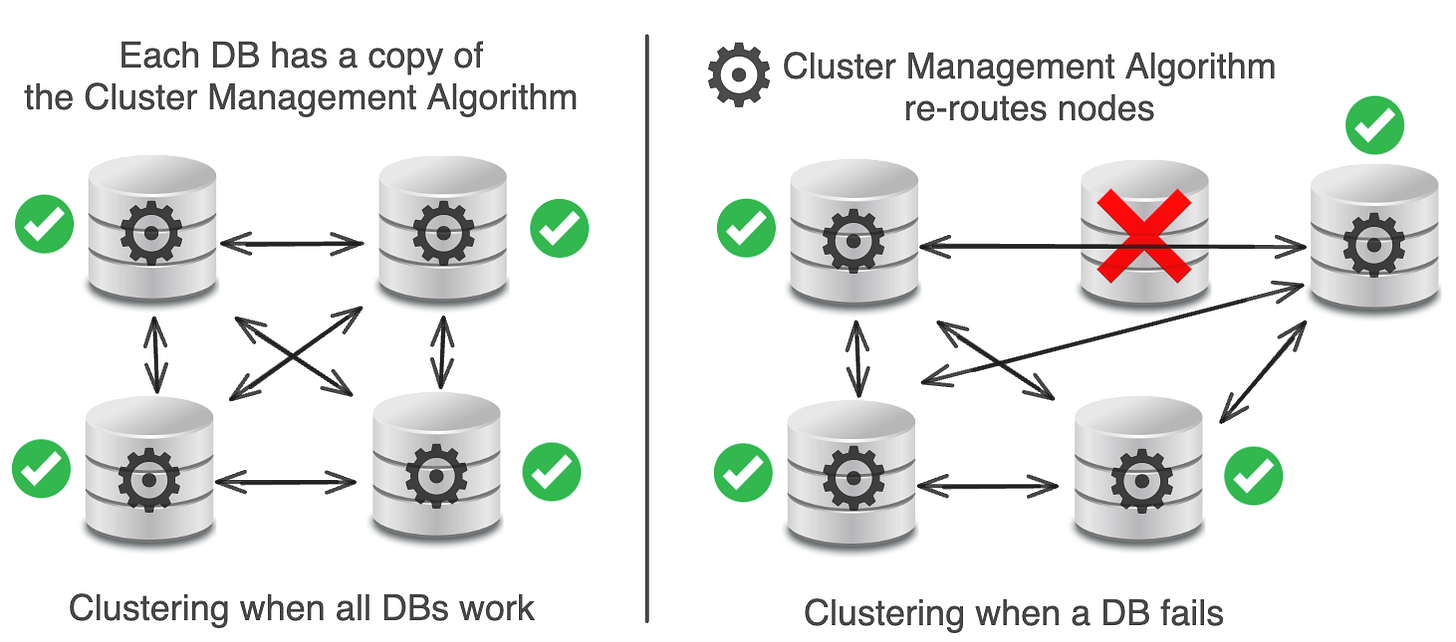
Database clustering is the process of connecting multiple database servers to work together as a single system.
In theory, clustering automatically scales datastores, provides high availability, free load balancing, and doesn’t have a single point of failure.
Unfortunately, in practice, clustering was overly complex, had difficult upgrade mechanisms, and it had a big single point of failure.
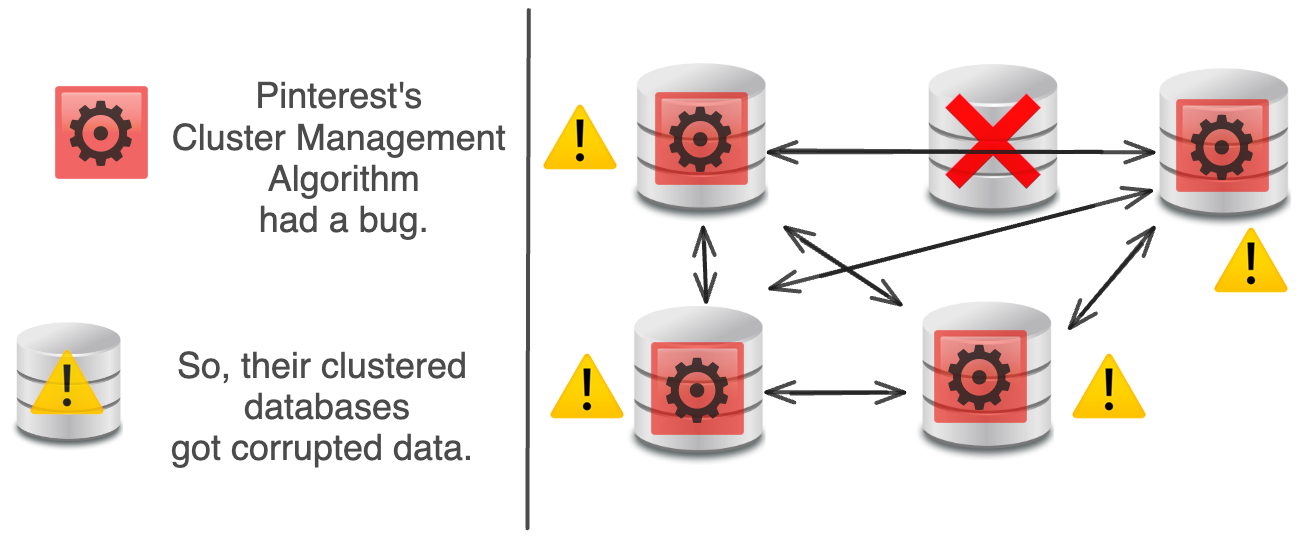
Each DB has a Cluster Management Algorithm that routes from DB to DB.
When something goes wrong with a DB, a new DB is added to replace it.
In theory, the Cluster Management Algorithm should handle this just fine.
In reality, there was a bug in Pinterest’s Cluster Management Algorithm that corrupted data on all their nodes, broke their data rebalancing, and created some unfixable problems.
Pinterest’s solution? Remove all clustering tech (Cassandra, Membase) from the system. Go all-in with MySQL + Memcached (more proven).
MySQL and Memcached are well-proven technologies. Facebook used the two to create the largest Memcached system in the world, which handled billions of requests per second for them with ease.
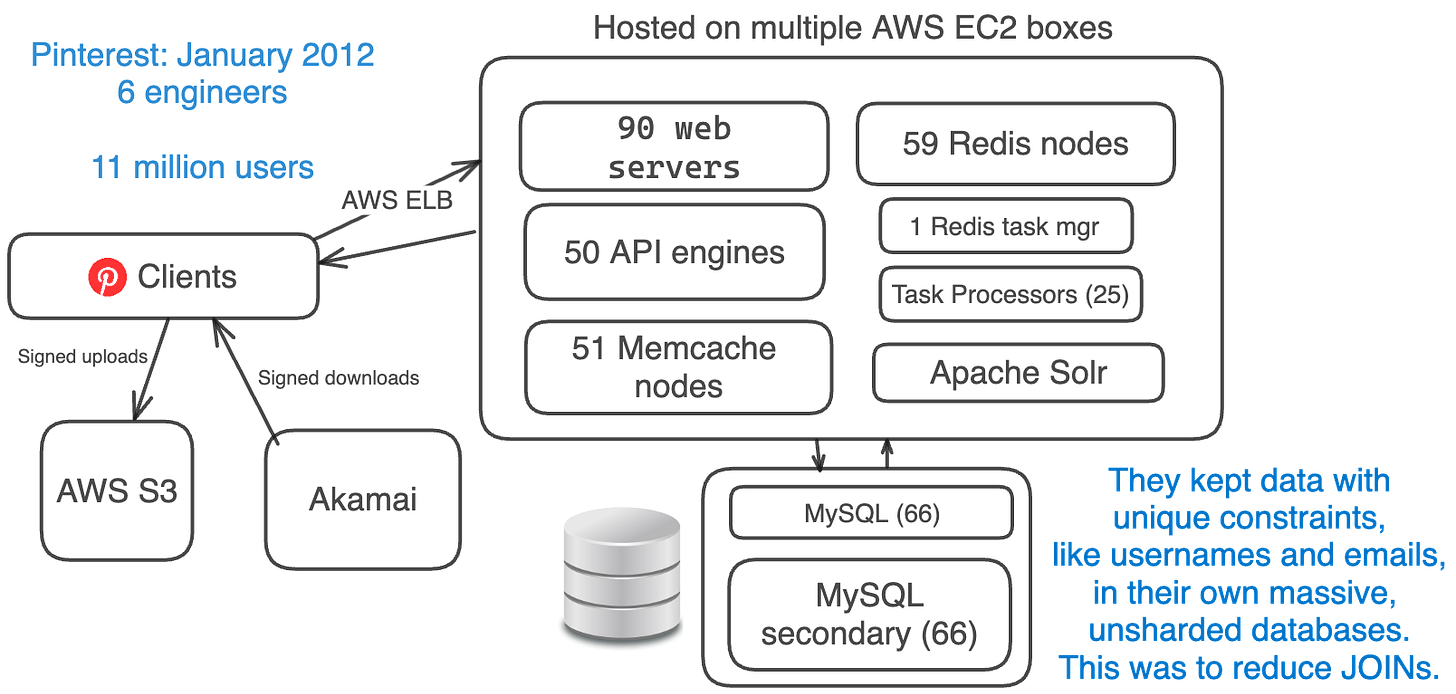
In January 2012, Pinterest was handling ~11 million monthly active users, with anywhere between 12 million to 21 million daily users.
At this point, Pinterest had taken the time to simplify their architecture.
They removed less-proven ideas, like clustering and Cassandra at the time, and replaced them with proven ones, like MySQL, Memcache, and sharding.
Their simplified stack:
- Amazon EC2 + S3 + Akamai (replaced CloudFront)
- AWS ELB (Elastic Load Balancing)
- 90 Web Engines + 50 API Engines (using Flask)
- 66 MySQL DBs + 66 secondaries
- 59 Redis Instances
- 51 Memcache Instances
- 1 Redis Task Manager + 25 Task Processors
- Sharded Apache Solr (replaced Elasticsearch)
- Removed Cassanda, Membase, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, NGINX
Database sharding is a method of splitting a single dataset into multiple databases.
Benefits: high availability, load balancing, simple algorithm for placing data, easy to split databases to add more capacity, easy to locate data
When Pinterest first sharded their databases, they had a feature freeze. Over the span of a few months, they sharded their databases incrementally and manually:
The team removed table joins and complex queries from the database layer. They added lots of caching.
Since it was extra effort to maintain unique constraints across databases, they kept data like usernames and emails in a huge, unsharded database.
All their tables existed on all their shards.
Since they had billions of “pins”, their database indexes ran out of memory.
They would take the largest table on the database and move it to its own database.
Then, when that database ran out of space, they would shard.
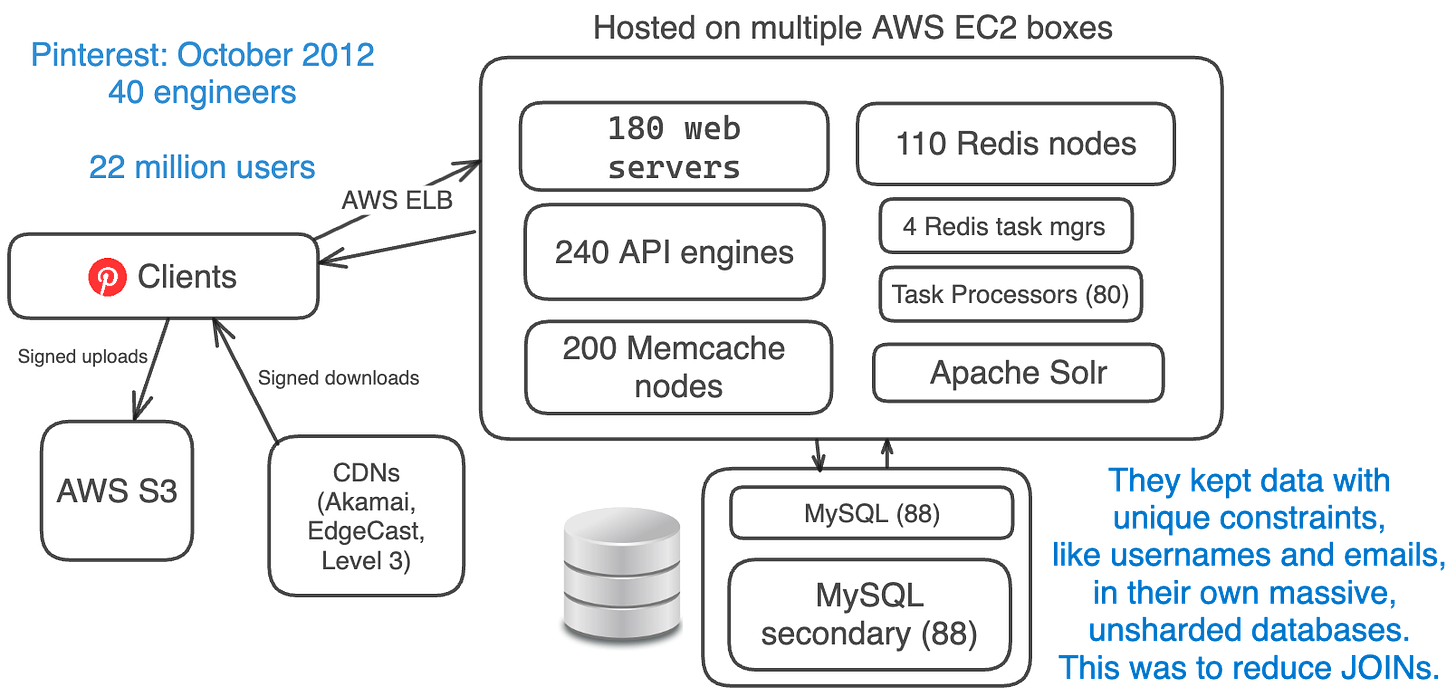
In October 2012, Pinterest had around 22 million monthly users, but their engineering team had quadrupled to 40 engineers.
The architecture was the same. They just added more of the same systems.
- Amazon EC2 + S3 + CDNs (EdgeCast, Akamai, Level 3)
- 180 web servers + 240 API engines (using Flask)
- 88 MySQL DBs + 88 secondaries each
- 110 Redis instances
- 200 Memcache instances
- 4 Redis Task Managers + 80 Task Processors
- Sharded Apache Solr
They started moving from hard disk drives to SSDs.
An important lesson learned: limited, proven choices was a good thing.
Sticking with EC2 and S3 meant they had limited configuration choices, leading to less headaches and more simplicity.
However, new instances could be ready in seconds. This meant that they could add 10 Memcache instances in a matter of minutes.
SWE Quiz is a compilation of 450+ software engineering and system design questions covering databases, authentication, caching, etc.
They’ve been created by engineers from Google, Meta, Apple, and more.
Identify and fix gaps in your software knowledge + pass the “software trivia” questions during interviews.
Like Instagram, Pinterest had a unique ID structure because they had sharded databases.
Their 64-bit ID looked like:
Shard ID: which shard (16 bits)
Type: object type, such as pins (10 bits)
Local ID: position in table (38 bits)
The lookup structure for these IDs was a simple Python dictionary.
They had Object tables and Mapping tables.
Object tables were for pins, boards, comments, users, and more. They had a Local ID mapped to a MySQL blob, like JSON.
Mapping tables were for relational data between objects, like mapping boards to a user or likes to a pin. They had a Full ID mapped to a Full ID and a timestamp.
All queries were PK (primary key) or index lookups for efficiency. They cut out all JOINs.
This article is based on Scaling Pinterest, a talk given by the Pinterest team in 2012.